Land O’Lakes, the Minnesota-based dairy cooperative, expects to sell 275 million to 300 million pounds of the stuff this year — a 20% increase — as rising retail demand more than makes up for lost restaurant business. Nationwide, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, butter production is up 6% over the first nine months of the year and is on track to top two billion pounds for the first time since 1943.
This year’s boom is, as is apparent from the chart, part of a longer-term comeback. On a per-capita basis, Americans eat far less butter than they did in the early decades of the 20th century. But they eat more than they did in the 1980s and 1990s.
After staving off competition from margarine with nearly a century of lobbying for margarine bans, taxes and color restrictions, butter producers lost their regulatory advantages in the 1940s and 1950s and ceded a lot of market share to the cheaper spread — which had originally been derived from beef fat but was by then mainly made out of vegetable oil. As medical researchers began to link consumption of animal fats with heart disease in the 1950s and 1960s, margarine gained even more ground as a purportedly healthier alternative.
Those health claims were later mostly debunked, and the price difference between butter and margarine began to matter less as incomes rose and families shrank (food purchased for off-premises consumption accounted for more than 18% of consumer spending in the early 1950s and just 6% in 2019).
Butter also benefited from the emphasis on genuine ingredients accompanying the good-food revival that began in the 1960s (Julia Child certainly wasn’t going to use margarine). And let’s be honest, it tastes better. Corn oil, olive oil and other vegetable oils now play a much bigger role in American diets than they used to, so butter will probably never regain its central status of a century ago. But it’s not going away.
“It’s a survivor story,” says Peter Vitaliano, vice president of economic policy and market research at the National Milk Producers Federation.
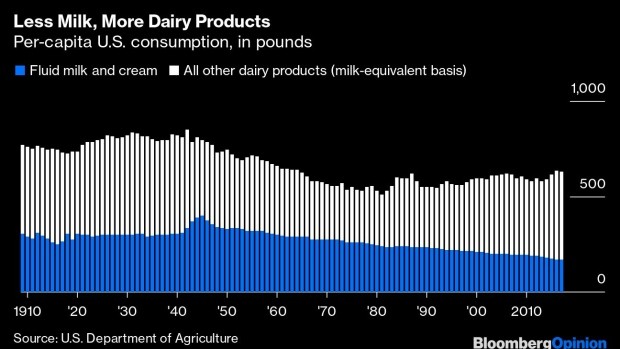
The same goes for the dairy industry in general. It can seem awfully embattled from time to time, and for good reason. Giant, highly productive dairies have been driving lots of smaller farmers out of business. Competition from “milks” made of almonds, oats, soybeans and other plants has taken market share from the real thing and led to a dairy industry lobbying campaign reminiscent of the margarine wars of yore. President Donald Trump’s trade policies have caused problems too. Two big milk marketers, Borden Dairy Co. and Dean Foods Inc., have filed for bankruptcy in the past 12 months.
But the big picture for the industry since 1980 or so is of declining demand for its core product (milk, that is) being more than offset by rising sales of almost everything that can be made out of milk.
Even within milk sales there’s been an interesting shift lately, with whole milk outselling 2% milk for the first time in 15 years in 2018 and building on its lead in 2019, and skim milk sales drifting downward. If you’re going to drink milk, and not smashed-up almonds mixed with water, then you might as well drink the milkiest kind of milk.
Whole milk happens to be the most profitable product for dairy farmers, as it’s basically just what comes out of the cow and thus doesn’t require them to share much revenue with processors. It also has benefited from the new eat-at-home normal of the pandemic, with sales up 4.1% through August (2% milk sales are up too, with skim and 1% down).
But on the whole, it is products made of milk that have kept the industry going. The butter revival is one aspect of this. The rise of yogurt, which was close to nonexistent in the U.S. before the 1970s, is another, even though it has faded a bit lately.
The main driver of the dairy industry’s resilience, though, has been cheese. Americans consume almost three times as much of it per-person as they did in 1970.
Not all of this is the result of what you’d call organic consumer demand. Yes, the big gains in Italian cheese consumption seem to reflect the fact that we eat a lot more pizza than we used to. One can also see hints in the data of the rising popularity of Mexican food (which in its north-of-the-border incarnation contains lots of Cheddar and Jack cheese), bagels’ emergence from regional-food status (cream cheese!) and other fun food trends.
But as cheese can be stored for longer than milk or butter or yogurt, it’s also something the dairy industry makes when it has more milk than it knows what to do with, resulting in the infamous “cheese mountain” that is occasionally reduced in size by big government purchases. Those have been especially big this year, with the Agriculture Department so far delivering more than 118 million food boxes — each containing several pounds of dairy products, mainly cheese — to food banks and other charities as part of pandemic-relief efforts.
The industry has also found new things to sell beyond milk, butter, yogurt and cheese, and new places to sell them. Forty years ago the U.S. hardly exported any dairy products. Now it exports a fair amount of cheese, mainly to Mexico, South Korea and Japan, and even bigger quantities of cheese-making byproducts such as whey powder, whey protein isolate and lactose, all of which are used in manufacturing foods and dietary supplements.
The main byproduct of modern butter-making is skim milk powder, most of which is exported to Mexico and Southeast Asia to be reconstituted, often in combination with vegetable oils, into various milk-like drinks. Overall, says Vitaliano, the U.S. exports about 4% of the milk fat it produces and 19% of the skim solids.
To bring things back to butter, the U.S. actually imports more of the stuff than it exports, with Ireland’s Kerrygold the No. 2 butter brand in the U.S. after Land O’Lakes. But the import quantities are still small relative to domestic production. So this year of high butter demand has been good for U.S. dairy cooperatives that specialize in the stuff, such as Land O’Lakes and No. 1 producer California Dairies Inc., which makes Challenge and Danish Creamery butter. (Both Land O’Lakes and California Dairies also produce private-label butter for retailers, so their role in supplying the country with butter goes way beyond their own brands.)
It has also been a good year for California dairies in general, given that the state accounts for just over 30% of U.S. butter production, with Land O’Lakes a big presence there too. Wisconsin, “America’s Dairyland,” focuses more on cheese, with a quarter of U.S. production. New York is tops in yogurt, with about 15% of production.
In terms of milk output for all purposes, California is No. 1 at more than 18% of the national total. It has held the top spot since passing Wisconsin in 1993, but the latter has been narrowing the gap lately. Idaho recently overtook New York for third place, and Texas may be nipping at its heels soon. For an ancient, not exactly fast-growing industry, dairy has a lot more drama than you might expect.
This column does not necessarily reflect the opinion of the editorial board or Bloomberg LP and its owners.
Justin Fox is a Bloomberg Opinion columnist covering business. He was the editorial director of Harvard Business Review and wrote for Time, Fortune and American Banker. He is the author of “The Myth of the Rational Market.”