Guy Trafford is watching how Australian farmers are reacting to the expectation that drought conditions are returning there, and how that is affecting prices for what we are selling.
On the back of the poor returns being experienced by New Zealand sheep farmers in particular, much of the ‘over supply’ into reduced demand areas is being ‘blamed’ upon Australian farmers. While this is superficially correct, no blame should be placed upon the Australian farmers. They, as are New Zealand farmers are nervous (perhaps extremely in Australia) of the impending onset of the El Nino weather conditions.
Australian droughts and weather extremes tends to be several degrees greater than they are over here. The map below shows already that widespread dry areas are becoming apparent. This is despite the accompanying narrative saying that to date (mid November) “conditions have been better than expected for fodder production”. However, there is nothing like the potential threat of a drought to catch farmers attention, hence the greater than normal destocking.
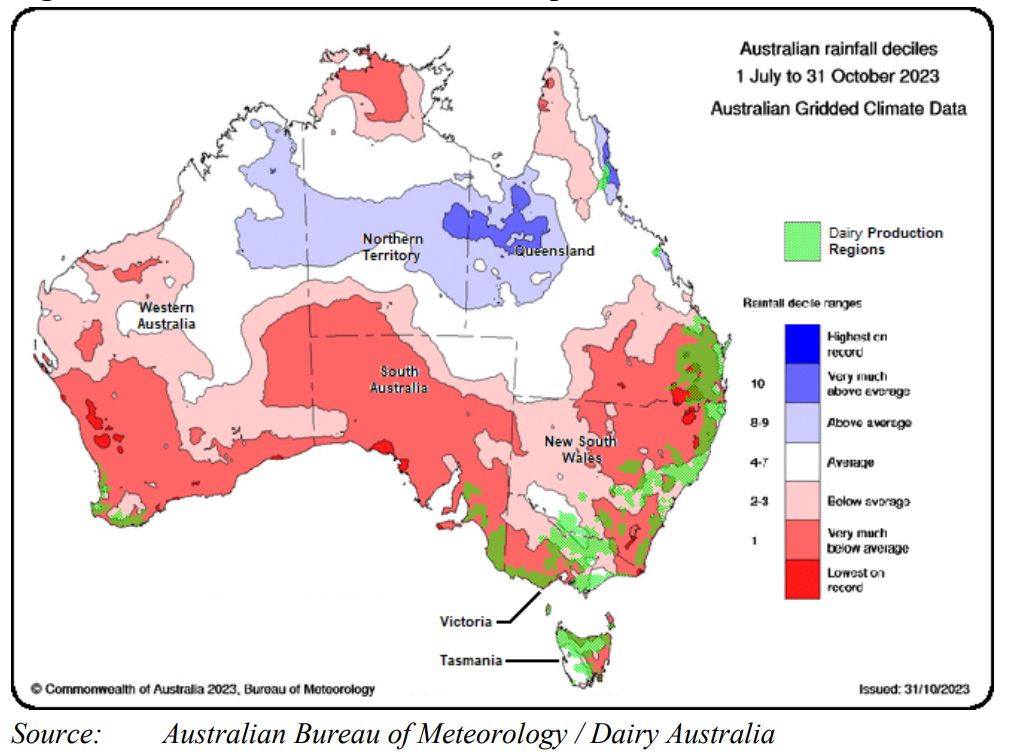
According to the MLA site the Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) numbers were reflecting the drier conditions experienced in many parts of Australia over winter and earlier spring with producers’ responding to the forecast of the El Nino summer.
The latest ABS statistics for the September quarter showed a 5.7% increase in red meat production, with cattle slaughter increased by 10.5% to 1.9 million head and overall beef production up 8.3% to 589,406 tonnes. Lamb slaughter in the September 2023 quarter increased 8.7% to 6.6 million head and lamb meat production increased 7.7% to 160,954 tonnes.
This additional supply onto an already depressed market is why New Zealand farmers are seeing prices fall.
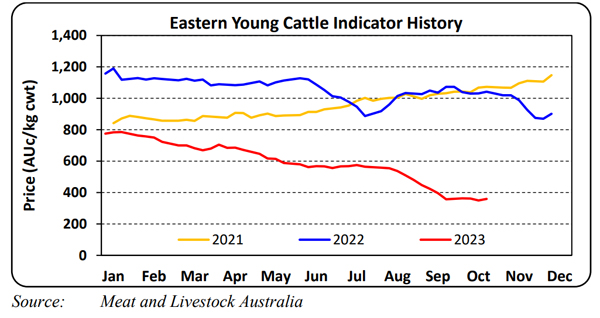
Ironically Australian mature sheep slaughter, in contrast, decreased by 18.1% to 2.1 million head, with mutton production back 11.8% to 54,189 tonnes, with the decrease largely due to elevated lamb slaughter reducing sheep processing capacity. Since the end of the September quarter slaughter numbers of lambs have dropped back on previous weeks and perhaps with the reduced numbers prices have lifted somewhat. The heavy lamb indicator rose by 13cents from last week to end at 499¢/kg carcass weight. This compares to New Zealand returning an average of 612c NZ$ or 565c when converted to A$.
So, neither country are getting rich on the back of sheep. Forward steers which are going onto the feedlots have shown a recent lift by 21¢ to 238c/kg lwt again New Zealand prices compare well although not stunning with forward 2yr steers around the 305c per kg NZ$ or around 282c A$.
When it comes to dairy Australia appears to be faring better as the graph below shows.
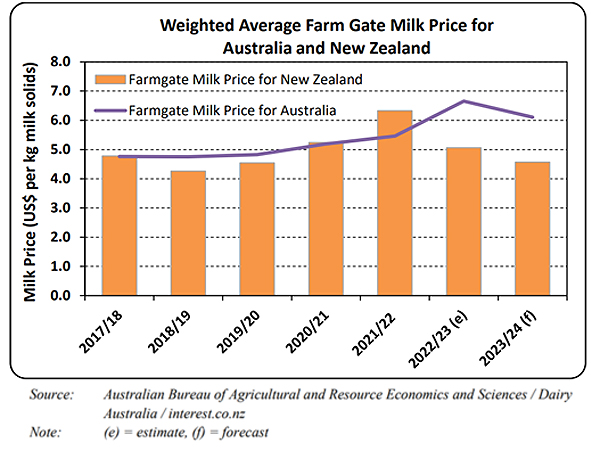
The difference can be largely put down to the larger domestic market providing a stronger base, particularly when the international market is weaker.
The 2022-23 season has had the highest farm gate price for milk and this season predicted to be the second-best season price wise. Australia only exports 35% of its production compared to 90% for New Zealand. Of all of their milk production, 28.5% is consumed as fresh milk although overall in the last 5 years milk products consumed locally are averaging a downward trend of around -0.6% annually.
Domestic milk prices vary from one manufacturer to the next and from region to region. Areas that almost exclusively supply the liquid milk market for domestic consumption receive the highest milk prices, whereas for those regions where most of the milk is used for manufactured products, the milk price to dairy farmers is lowest.
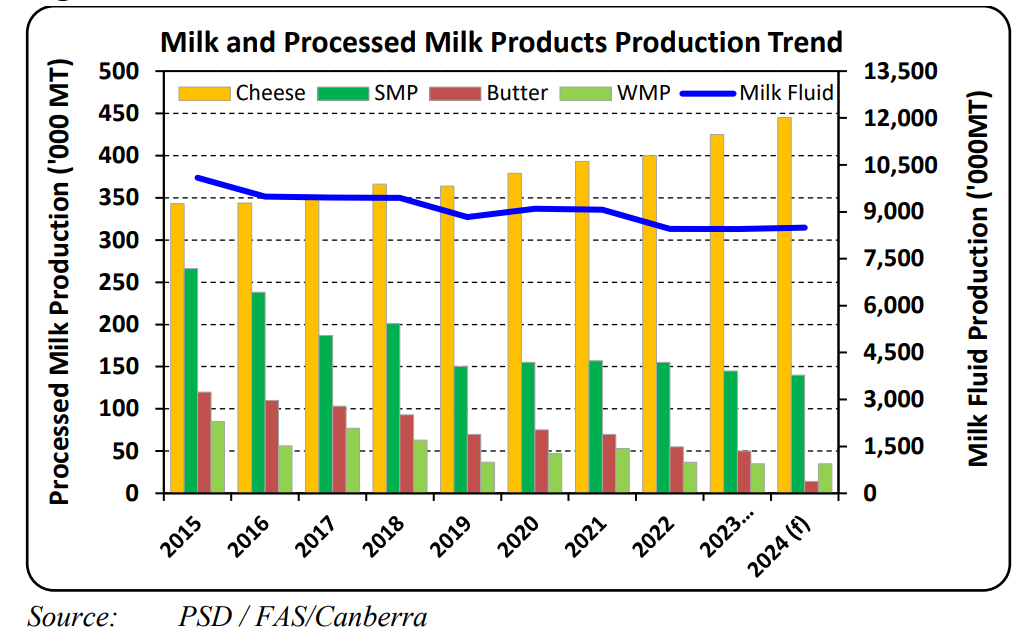
Production this year so far is up slightly. The bulk of processed milk goes into cheese production, (42%) which has also been giving better returns than alternative products. Butter, WMP are also produced and fresh milk is also exported around Asia (China in particular) and the Pacific. Unlike New Zealand’s other major trading partners, Australia is a net exporter of cheese and can supply much of its domestic needs. Imports of New Zealand cheese to Australia have typically been the lower value cheddar type cheeses, while Australian processors increasingly focus on producing more specialized cheeses for export.
Much of New Zealand’s price advantage over Australia producers is due to the low milk price farmers receive here. The same ‘advantage’ also applies to butter with New Zealand providing 85% of Australian butter imports.
Despite a small rise in production in the last season (2022-23) over the previous, overall dairying in general is in decline. As the graph shows milk production is holding more steady than farms and herd size. Perhaps indicating that more marginal farms are the ones exiting the industry. It appears that the bulk of these farms were joining the beef industry, at least up until recently.
Labour shortages are given as one of the biggest issues within the dairy industry and also as at least a partial reason for exiting with beef farming requiring less labour inputs and recently receiving good returns being attractive to shift into.
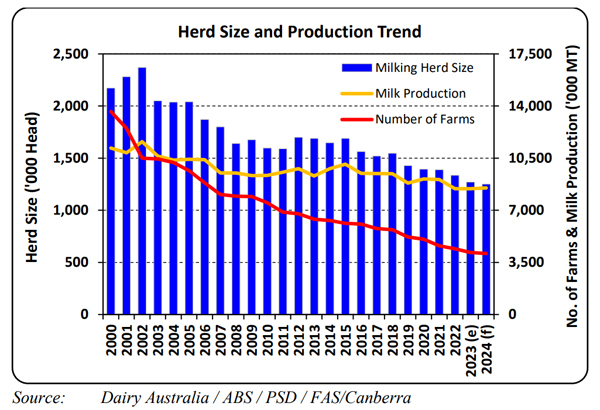
Lately with beef prices falling the exiting of dairying to beef has all but ceased.
One additional cost many Australian dairy farmers contend with is the cost of water. This year storage dams etc are said to be at good levels at least for now.
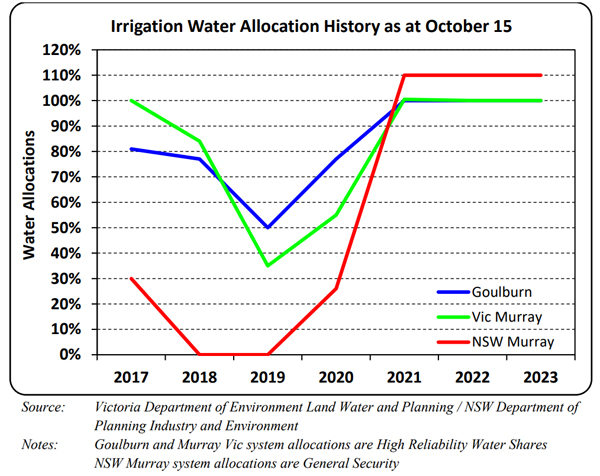
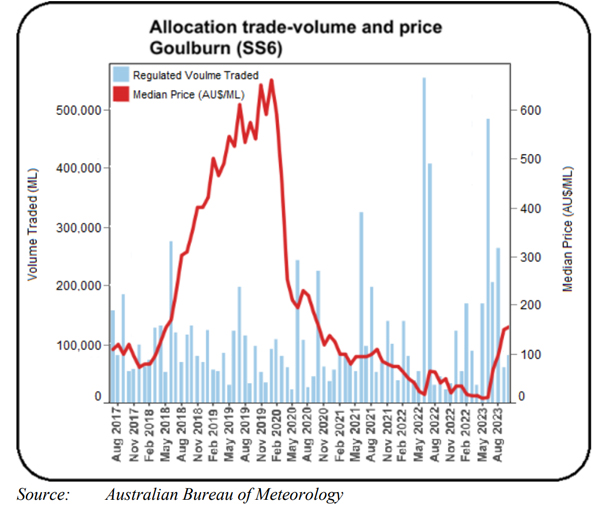
For the Goulburn irrigation system, which supplies the largest irrigation-dependent dairy farming region in northern Victoria, traded water in the current 2023-24 irrigation season has risen to around AU$160 per million litres which is far below the peak of over AU$600/ML paid during the drought in 2019 (see graph below).
Although this is still substantially higher than the previous two seasons, now that the spring fodder production period is near complete, any further rise in the price of traded irrigation water will have little impact on dairy farmers, who generally do not have perennial pastures requiring water allocations. But it will impact those who irrigate corn and alfalfa crops over the summer months for silage production.
When it comes to competing on international dairy markets, while Australia does have an impact especially as its supply comes on stream at similar times to New Zealand milk products. However, it’s volumes especially in the processed lines are not huge. New Zealand’s total milk production is around 21 billion litres compared to Australia 8.8 billion litres (of which a large slice remains as liquid milk).
Unlike dairy, Australia has the third largest sheep flock (nearly 75 million), is the world’s largest sheep meat exporter, and so what and where it does with sheep meat certainly has an impact upon New Zealand exporters and producers. Perhaps we are fortunate that Australian dairying does not have the same status.
























